nProfiler® 1 Stomach Cancer Assay의 안전성과 신뢰성의 근거는 분석적 성능시험 및 임상적 성능시험의 결과와 해당 기술을 활용한 임상결과의 논문 게재입니다.
노보믹스는 지난 2018년 Lancet Oncology와 Journal of Gastric Cancer에, 2019년에는 Yonsei Medical Journal에 논문을 게재했습니다.


CLASSIC(Adjuvant capecitabine and oxaliplatin for gastric cancer after D2 gastrectomy) 임상은 임상3상으로 위암수술 후 보조항암요법의
생존편익 여부를 검정하기 위해 중국, 대만, 한국 35개 기관에서 2006년부터 2010년까지 1,035명의 위암 환자를 대상으로 진행한 무작위 전향임상입니다.
(Clinicaltrials.gov 등록번호 NCT03403296)
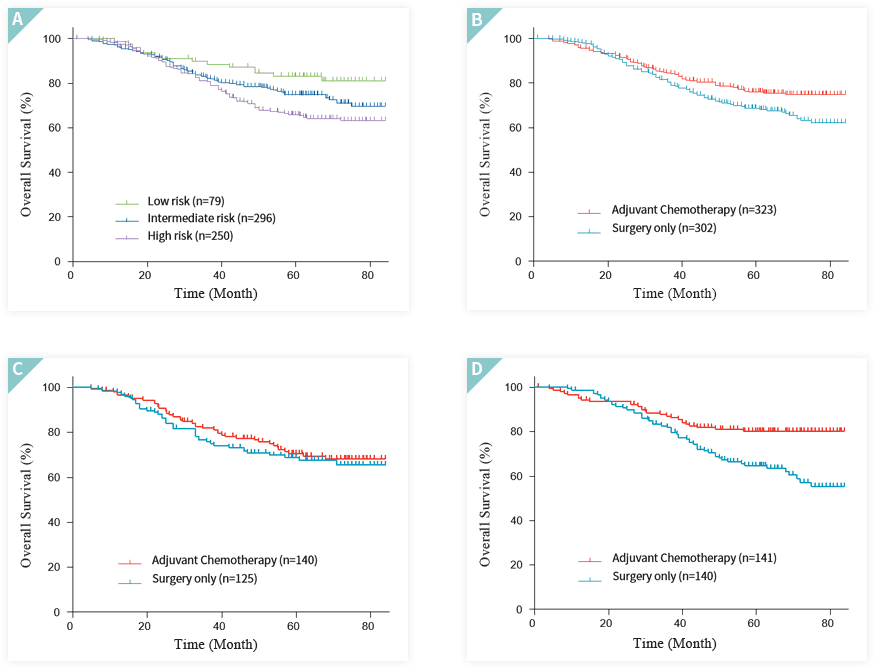
nProfiler®1 은 1,035명의 환자 샘플의 대표성을 확보할 수 있는 629개의 샘플을 예후군 구분 및 예후군 별 생존율을 추적 관찰했습니다.
예후군 별 5년 생존율 분석결과 nProfiler® 1으로 구분된 저위험군에서 83.2%, 중위험군에서 74.8%, 고위험군에서 66.0%의 5년 생존율을 확인했습니다.
또한 로그랭크 검정을 통해 예후군 사이에 유의한 차이가 있는지를 확인했습니다 (p-value = 0.012). nProfiler® 1 을 통해 항암생존편익여부에 따라 편익군과 비편익군으로
구분하였을 때, 항암생존편익군에서는 항암치료 여부에 따라 5년 생존율이 64.5%에서 80.0%로 향상된 반면, 항암생존비편익군에서는 항암치료 여부에 따라 5년 생존율이
72.9%에서 72.5%로 차이를 보이지 않음을 확인했습니다.
특히, 항암생존비편익군으로 분류되는 저위험군 환자의 경우 다변수 콕스 회귀분석에서 항암치료를 받은 환자의 위험비는 항암치료를 받지 않은 환자에 대해
각각 1.21 (p-value = 0.72)과 1.65(p-value = 0.40)로 관찰되어 예후가 좋은 환자들이 항암치료에 생존이익이 없음을 확인했습니다.
Cheong JH, Yang HK, Kim H, Kim WH, Kim YW, Kook MC, Park YK, Kim HH, Lee HS, Lee KH, Gu MJ, Kim HY, Lee J, Choi SH, Hong S, Kim JW,
Choi YY, Hyung WJ, Jang E, Kim H, Huh YM, Noh SH. Predictive test for chemotherapy response in resectable gastric cancer: a multi-cohort,
retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2018 May;19(5):629-638.
1: Xiao X, Chen W, Wei ZW, Chu WW, Lu XF, Li B, Chen H, Meng SJ, Hao TF, Wei JT, He YL, Zhang CH. The Anti-Tumor Effect of Nab-Paclitaxel Proven by Patient-Derived Organoids. Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Jun 24;13:6017-6025. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S237431. PMID: 32612367; PMCID: PMC7322144.
2: Koushyar S, G Powell A, Vincan E, J Phesse T. Targeting Wnt Signaling for the Treatment of Gastric Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 30;21(11):3927. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113927. PMID: 32486243; PMCID: PMC7311964.
3: Yoon SJ, Park J, Shin Y, Choi Y, Park SW, Kang SG, Son HY, Huh YM. Deconvolution of diffuse gastric cancer and the suppression of CD34 on the BALB/c nude mice model. BMC Cancer. 2020 Apr 15;20(1):314. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-06814-4. PMID: 32293340; PMCID: PMC7160933.
4: Park SY, Lee YJ, Park J, Kim TH, Hong SC, Jung EJ, Ju YT, Jeong CY, Park HJ, Ko GH, Song DH, Park M, Yoo J, Jeong SH. PRDX4 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. 2020 May;19(5):3522-3530. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11468. Epub 2020 Mar 19. PMID: 32269626; PMCID: PMC7114939.
5: Li B, Jiang Y, Li G, Fisher GA Jr, Li R. Natural killer cell and stroma abundance are independently prognostic and predict gastric cancer chemotherapy benefit. JCI Insight. 2020 May 7;5(9):e136570. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.136570. PMID: 32229725; PMCID: PMC7253031.
6: Li R, Liu H, Cao Y, Wang J, Chen Y, Qi Y, Lv K, Liu X, Yu K, Lin C, Zhang H, He H, Li H, Chen L, Shen Z, Qin J, Zhang W, Sun Y, Xu J. Identification and validation of an immunogenic subtype of gastric cancer with abundant intratumoural CD103+CD8+ T cells conferring favourable prognosis. Version 2. Br J Cancer. 2020 May;122(10):1525-1534. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-0813-y. Epub 2020 Mar 24. PMID: 32205862; PMCID: PMC7217759.
7: Di Bartolomeo M, Morano F, Raimondi A, Miceli R, Corallo S, Tamborini E, Perrone F, Antista M, Niger M, Pellegrinelli A, Randon G, Pagani F, Martinetti A, Fucà G, Pietrantonio F; ITACA-S study group. Prognostic and Predictive Value of Microsatellite Instability, Inflammatory Reaction and PD-L1 in Gastric Cancer Patients Treated with Either Adjuvant 5-FU/LV or Sequential FOLFIRI Followed by Cisplatin and Docetaxel: A Translational Analysis from the ITACA-S Trial. Oncologist. 2020 Mar;25(3):e460-e468. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0471. Epub 2019 Nov 25. PMID: 32162808; PMCID: PMC7066701.
8: Chen Q, Gao P, Song Y, Huang X, Xiao Q, Chen X, Lv X, Wang Z. Predicting the effect of 5-fluorouracil-based adjuvant chemotherapy on colorectal cancer recurrence: A model using gene expression profiles. Cancer Med. 2020 May;9(9):3043-3056. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2952. Epub 2020 Mar 9. PMID: 32150672; PMCID: PMC7196071.
9: Wu M, Ding Y, Jiang X, Chen Y, Wu N, Li L, Wang H, Huang Y, Xu N, Teng L. Overexpressed MAGP1 Is Associated With a Poor Prognosis and Promotes Cell Migration and Invasion in Gastric Cancer. Front Oncol. 2020 Jan 17;9:1544. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01544. PMID: 32010630; PMCID: PMC6978879.
10: Kim DG, An JY, Kim H, Shin SJ, Choi S, Seo WJ, Roh CK, Cho M, Son T, Kim HI, Cheong JH, Hyung WJ, Noh SH, Choi YY. Clinical Implications of Microsatellite Instability in Early Gastric Cancer. J Gastric Cancer. 2019 Dec;19(4):427-437. doi: 10.5230/jgc.2019.19.e38. Epub 2019 Nov 8. PMID: 31897345; PMCID: PMC6928080.
11: Kim BK, Cheong JH, Im JY, Ban HS, Kim SK, Kang MJ, Lee J, Kim SY, Park KC, Paik S, Won M. PI3K/AKT/β-Catenin Signaling Regulates Vestigial-Like 1 Which Predicts Poor Prognosis and Enhances Malignant Phenotype in Gastric Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2019 Dec 3;11(12):1923. doi: 10.3390/cancers11121923. PMID: 31816819; PMCID: PMC6966677.
12: Di Bartolomeo M, Morano F, Raimondi A, Miceli R, Corallo S, Tamborini E, Perrone F, Antista M, Niger M, Pellegrinelli A, Randon G, Pagani F, Martinetti A, Fucà G, Pietrantonio F; ITACA‐S study group. Prognostic and Predictive Value of Microsatellite Instability, Inflammatory Reaction and PD-L1 in Gastric Cancer Patients Treated with Either Adjuvant 5-FU/LV or Sequential FOLFIRI Followed by Cisplatin and Docetaxel: A Translational Analysis from the ITACA-S Trial. Oncologist. 2019 Nov 25: theoncologist.2019-0471. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0471. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 31767795.
13: Liu T, Fang P, Han C, Ma Z, Xu W, Xia W, Hu J, Xu Y, Xu L, Yin R, Wang S, Zhang Q. Four transcription profile-based models identify novel prognostic signatures in oesophageal cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Jan;24(1):711-721. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14779. Epub 2019 Nov 19. PMID: 31746108; PMCID: PMC6933393.
14: Jeon J, Cheong JH. Clinical Implementation of Precision Medicine in Gastric Cancer. J Gastric Cancer. 2019 Sep;19(3):235-253. doi: 10.5230/jgc.2019.19.e25. Epub 2019 Aug 12. PMID: 31598369; PMCID: PMC6769368.
15: Zubarayev M, Min EK, Son T. Clinical and molecular prognostic markers of survival after surgery for gastric cancer: tumor-node-metastasis staging system and beyond. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Aug 20;4:59. doi: 10.21037/tgh.2019.08.05. PMID: 31559340; PMCID: PMC6737396.
16: Ho SWT, Tan P. Dissection of gastric cancer heterogeneity for precision oncology. Cancer Sci. 2019 Nov;110(11):3405-3414. doi: 10.1111/cas.14191. Epub 2019 Sep 25. PMID: 31495054; PMCID: PMC6825006.
17: Hwang JE, Kim H, Shim HJ, Bae WK, Hwang EC, Jeong O, Ryu SY, Park YK, Cho SH, Chung IJ. Lymph-node ratio is an important clinical determinant for selecting the appropriate adjuvant chemotherapy regimen for curative D2-resected gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019 Aug;145(8):2157-2166. doi: 10.1007/s00432-019-02963-7. Epub 2019 Jul 4. PMID: 31273512.
18: Suenaga Y, Kanda M, Ito S, Mochizuki Y, Teramoto H, Ishigure K, Murai T, Asada T, Ishiyama A, Matsushita H, Tanaka C, Kobayashi D, Fujiwara M, Murotani K, Kodera Y. Prognostic significance of perioperative tumor marker levels in stage II/III gastric cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2019 Jan 15;11(1):17-27. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i1.17. PMID: 30984347; PMCID: PMC6451928.
19: Harada H, Hosoda K, Moriya H, Mieno H, Ema A, Ushiku H, Washio M, Nishizawa N, Ishii S, Yokota K, Tanaka Y, Kaida T, Soeno T, Kosaka Y, Watanabe M, Yamashita K. Cancer-specific promoter DNA methylation of Cysteine dioxygenase type 1 (CDO1) gene as an important prognostic biomarker of gastric cancer. PLoS One. 2019 Apr 1;14(4):e0214872. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214872. PMID: 30934021; PMCID: PMC6443169.
20: Chen Y, Wang D, Song Y, Zhang X, Jiao Z, Dong J, Lü L, Zou Z, Du W, Qu F. Functional polymorphisms in circadian positive feedback loop genes predict postsurgical prognosis of gastric cancer. Cancer Med. 2019 Apr;8(4):1919-1929. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2050. Epub 2019 Mar 7. PMID: 30843665; PMCID: PMC6488121.
21: Choi YY, Cho M, Kwon IG, Son T, Kim HI, Choi SH, Cheong JH, Hyung WJ. Ten Thousand Consecutive Gastrectomies for Gastric Cancer: Perspectives of a Master Surgeon. Yonsei Med J. 2019 Mar;60(3):235-242. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.3.235. PMID: 30799586; PMCID: PMC6391520.
22: Xu BB, Lu J, Zheng ZF, Xie JW, Wang JB, Lin JX, Chen QY, Cao LL, Lin M, Tu RH, Huang ZN, Lin JL, Zheng CH, Huang CM, Li P. The predictive value of the preoperative C-reactive protein-albumin ratio for early recurrence and chemotherapy benefit in patients with gastric cancer after radical gastrectomy: using randomized phase III trial data. Gastric Cancer. 2019 Sep;22(5):1016-1028. doi: 10.1007/s10120-019-00936-w. Epub 2019 Feb 9. PMID: 30739259.
23: Roh CK, Choi YY, Choi S, Seo WJ, Cho M, Jang E, Son T, Kim HI, Kim H, Hyung WJ, Huh YM, Noh SH, Cheong JH. Single Patient Classifier Assay, Microsatellite Instability, and Epstein-Barr Virus Status Predict Clinical Outcomes in Stage II/III Gastric Cancer: Results from CLASSIC Trial. Yonsei Med J. 2019 Feb;60(2):132-139. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.2.132. PMID: 30666834; PMCID: PMC6342711.
24: Jiang Y, Yuan Q, Lv W, et al. Radiomic signature of 18F fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT for prediction of gastric cancer survival and chemotherapeutic benefits. Theranostics. 2018;8(21):5915-5928. Published 2018 Nov 12. doi:10.7150/thno.28018
25: Jin M. Unique roles of tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase in immune control and its therapeutic implications. Exp Mol Med. 2019 Jan 7;51(1):1-10. doi: 10.1038/s12276-018-0196-9. PMID: 30613102; PMCID: PMC6321835.
26: Smyth EC, Nyamundanda G, Cunningham D, Fontana E, Ragulan C, Tan IB, Lin SJ, Wotherspoon A, Nankivell M, Fassan M, Lampis A, Hahne JC, Davies AR, Lagergren J, Gossage JA, Maisey N, Green M, Zylstra JL, Allum WH, Langley RE, Tan P, Valeri N, Sadanandam A. A seven-Gene Signature assay improves prognostic risk stratification of perioperative chemotherapy treated gastroesophageal cancer patients from the MAGIC trial. Ann Oncol. 2018 Dec 1;29(12):2356-2362. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy407. PMID: 30481267; PMCID: PMC6311954.
27: Lu J, Cao LL, Li P, Xie JW, Wang JB, Lin JX, Chen QY, Lin M, Tu RH, Huang CM, Zheng CH. Significance of Preoperative Systemic Immune Score for Stage I Gastric Cancer Patients. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2018 Jul 11;2018:3249436. doi: 10.1155/2018/3249436. PMID: 30116261; PMCID: PMC6079442.
28: Choi YY, Jang E, Seo WJ, Son T, Kim HI, Kim H, Hyung WJ, Huh YM, Noh SH, Cheong JH. Modification of the TNM Staging System for Stage II/III Gastric Cancer Based on a Prognostic Single Patient Classifier Algorithm. J Gastric Cancer. 2018 Jun;18(2):142-151. doi: 10.5230/jgc.2018.18.e14. Epub 2018 May 31. PMID: 29984064; PMCID: PMC6026714.


nProfiler® 1 을 검정한 3번의 임상 결과를 사후분석 해, nProfiler® 1의 예후군과 TNM 병기사이의 예후예측력의 보완적 관계를 검정하였습니다.
식약처 제705호 임상에 사용된 307개 검체의 임상시험 결과
식약처 제745호 임상에 사용된 652개 검체의 임상시험 결과
NCT03403296 임상에 사용된 625개 검체의 임상시험 결과
총 1,584명의 위암 환자 중 저위험군으로 분류된 187명의 환자가 기존 TNM 병기에서 한 단계씩 낮춰서 보완된 TNM 병기에 분류되어 병기 별 예후 예측력을 검정하였습니다.
| 기존 TNM 병기분류 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ⅡA | ⅡB | ⅢA | ⅢB | total | ||
| 보완된 TNM 병기분류 |
ⅠB | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| ⅡA | 126 | 57 | 0 | 0 | 183 | |
| ⅡB | 0 | 369 | 76 | 0 | 445 | |
| ⅢA | 0 | 0 | 531 | 44 | 575 | |
| ⅢB | 0 | 0 | 0 | 371 | 371 | |
| total | 136 | 426 | 607 | 415 | 1584 | |
기존 TNM 병기 대비 보완된 TNM 병기에서 예후 예측력의 C-index 값이 0.620에서 0.635로 향상됨을 확인했습니다.
환자의 치료지침 설계 시점에서 예후인자는 결정에 중요한 변수입니다. 유방암의 경우에는 해부학적 분류 모델인 TNM 병기 분류법에 종양생물 학적 정보를 반영하여
예후인자 계층화 모델을 정립하여 상용화하는 추세입니다. 아직 관련 연구가 부족한 위암에서도 이런 추세를 반영하여 예후 예측력 향상의 필요성이 있습니다.
Choi YY, Jang E, Seo WJ, Son T, Kim HI, Kim H, Hyung WJ, Huh YM, Noh SH, Cheong JH. Modification of the TNM Staging System for Stage II/III Gastric Cancer Based on a Prognostic Single Patient Classifier Algorithm. J Gastric Cancer.


CLASSIC 임상(NCT03403296)에 사용된 검체 중 MSI 및 EBV 상태 확인이 가능한 586개 검체의 임상시험 결과를 대상으로 MSI-high와 MSI-low/MSS, EBV(+)와 EBV(-) 각각에서 예후군 사이의 5년 생존율을 비교해 상호관계를 분석했습니다.
MSI-high 환자들이 상대적으로 MSI-low/MSS 환자들에 비해 예후가 좋으나, EBV infection 상태(+/-)에 따라 환자 사이에 예후 차이를 확인하 지 못했습니다.
MSI-low/MSS 환자들의 예후군은 통계적으로 유의미하게 구분됨을 확인했습니다. 특히 MSS/MSI-low이면서 저위험군인 환자들은 MSI-high환자와 같이 좋은 예후를
보이는 것을 확인했습니다. EBV는 상태에 상관없이 예후군이 잘 구분됨을 확인했습니다.
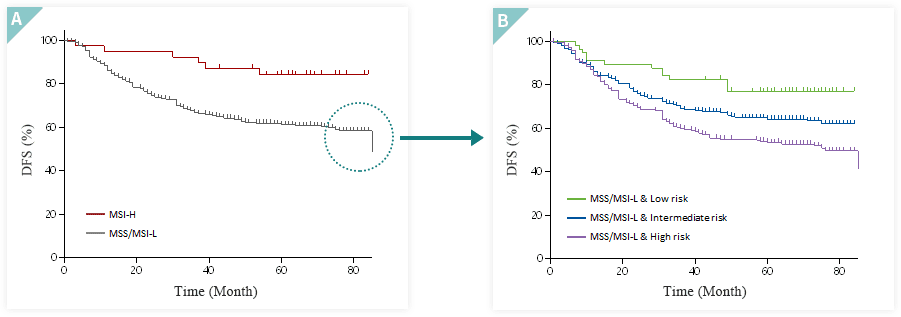
저위험군이면서 MSI-high인 경우가 13례 (저위험군 중 18.6%; p-value < 0.001), 저위험군이면서 EBV 양성인 경우가 22례 (저위험군 중 31.9%; p-value < 0.001)로
다른 예후군에 비해 저위험군에서 MSI 및 EBV와 통계적으로 높은 연관성을 보였습니다. MSI는 위암 예후예측 바이오마커로 알려지고 있으며,
nProfiler® 1 Stomach Cancer Assay로 구분된 예후군과 상호보완적으로 활용될 수 있습니다. 미국 및 유럽의 치료지침 가이드라인에서 MSI-high 대장암 환자들은
항암치료를 지양하고 있습니다. 위암에서도 MSI-high와 높은 상관성을 보이면서 항암 생존 비편익군인 저위험군 환자에게도 새로운 치료지침 설계의 필요성이 있습니다.
Roh CK, Choi YY, Choi S, Seo WJ, Cho M, Jang E, Son T, Kim HI, Kim H, Hyung WJ, Huh YM, Noh SH, Cheong JH. Single Patient Classifier Assay,
Microsatellite Instability, and Epstein-Barr Virus Status Predict Clinical Outcomes in Stage
II/III Gastric Cancer: Results from CLASSIC Trial. Yonsei Med J. 2019 Feb;60(2):132-139.